|
Thorotrast
•
Alpha-emitter
•
Previously used for cerebral angiography and liver/spleen imaging
• Use started in early 30s and continued to early 50s
• Excellent opacifying agent “well-tolerated“ by patients
• Could produce intense fibrosis in muscle if it extravasated on injection and
it was this side-affect which caused its use to be questioned first
•
Colloidal thorium dioxide deposited in liver (70%), spleen (30%), bone marrow,
lymph nodes
• Produces increased opacity of metal density in liver, spleen and celiac
nodes
• May be visualized in soft tissues of neck if extravasated there
•
Biologic half life of 400 years; physical half-life of 1010 years
•
Hepatic dose in 20 years about 1000-3000 rads
•
Produces angiosarcomas (hemangioendotheliomas) of liver (50%),
cholangiocarcinoma, hepatoma
• One of the causes of “bone-within-a-bone” in spine
• Long
latency period (25 years)
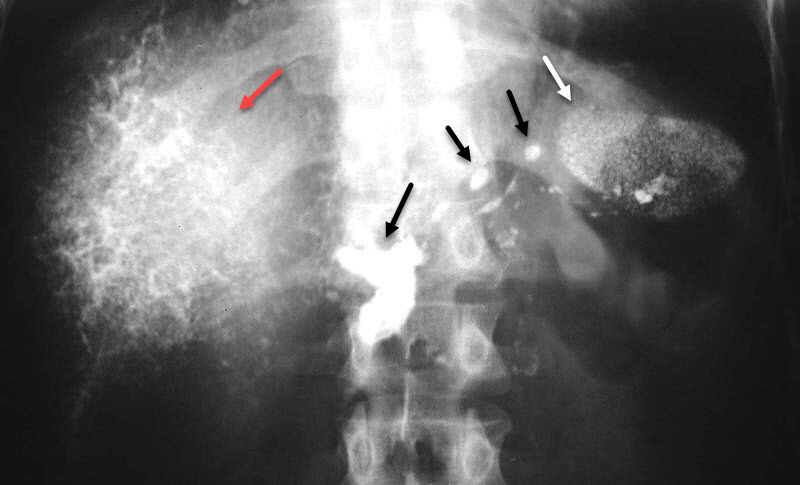
Thorotrast. Conventional radiograph of the upper abdomen shows dense Thorotrast residual contrast in the liver (red arrow), speckled throughout the spleen (white arrow) and particularly dense in the lymph nodes (black arrows).
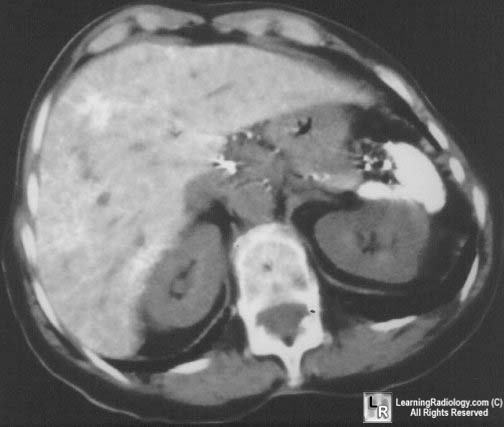
Thorotrast. There are dense deposits in the spleen, liver and lymph nodes from a prior injection of Thorotrast.
|