|
|
Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (GPA)
Formerly known as Wegener's Granulomatosis
General
-
Male:female
ratio of 2:1
-
Peak
in 40s
-
Autoimmune
disease characterized by necrotizing granulomas and angiitis
-
Diagnosis
is made by lung or kidney biopsy
-
Death
comes from renal failure or respiratory failure
-
Treated
with steroids and cytotoxic drugs
Respiratory
Tract (100% involved)
Upper respiratory
tract
Lungs
-
Multiple
nodules of varying sizes, especially at bases
-
Cavitate
frequently (50%)
-
Masses
wax and wane
-
Pleural
effusion (25%)
-
Alveolar
infiltrate occasionally
Other
Organs
-
Urinary
tract:focal glomerulonephritis (50%)
-
Joints:migratory
polyarthropathy (56%)
-
Skin:inflammatory
skin lesions (44%)
-
Eyes
and ears:proptosis and otitis media (29%)
-
Heart
and pericardium: myocardial infarction (28%)
-
CNS:
neuritis (22%)
Symptoms
-
Rhinorrhea
-
Sinusitis
-
Epistaxis
-
Cough
with hemoptysis
Midline
Lethal Granuloma
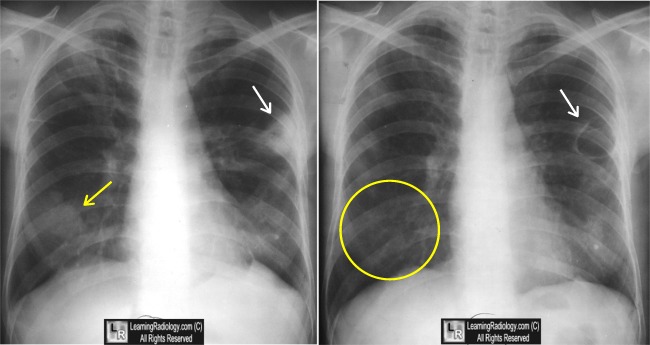 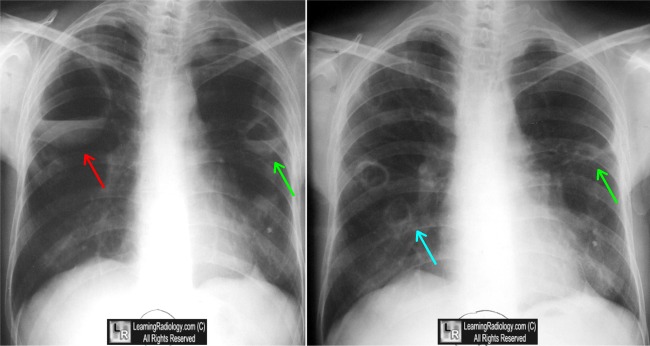
Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis. Four images span approximately two years and show typical waxing and waning of pulmonary masses (white and green arrows), some of which cavitate (blue arrow), some of which disappear over the course of time (yellow circle).
For this same photo without the annotations, click here and here
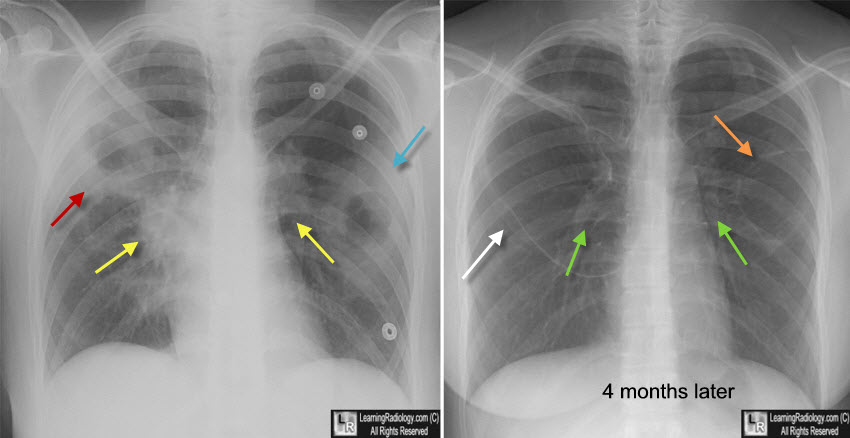
Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis. Two chest radiographs on the same patient 4 months apart show the marked changes in the appearances of the right upper lobe cavities (red and white arrows) and the left upper lobe cavities (blue and orange arrows). The patient's hilar adenopathy has markedly improved (yellow and green arrows).
Ravenel, JG, MD; Irshad, A, MD. Wegener Granulomatosis, Thoracic. eMedicine
King, TE, MD. Respiratory tract involvement in Wegener's granulomatosis. UpToDate
|
|
|