|
Histiocytosis X
Letterer-Siwe Disease
·
10%
of histiocytosis X
·
Acute
disseminated, fulminant form
·
Age
at onset
o
Several
weeks after birth to 2 years
·
Pathology
o
May
be confused with leukemia
·
Symptoms
o
Hemorrhage,
purpura
o
Severe
anemia
o
Fever
o
Hepatosplenomegaly
and lymphadenopathy
·
Bone
involvement in 50%
o
Widespread
lytic lesions
·
Prognosis:
70% mortality rate
Hand-Schuller-Christian
·
15-40%
of Histiocytosis X
·
Triad
of:
o
Exopthalmus
(33%)
o
Diabetes
insipidus (30-50%)
o
Lytic
skull lesions
·
Pathology
o
May
simulate Ewing's sarcoma
·
Age
at onset
o
5-10
years
·
Target
organs
o
Bone
§
Lytic skull lesions with
overlying soft tissue nodules
§
Large geographic skull lesions
§
"Floating teeth" with
mandibular involvement
o
Soft
tissue
§
Hepatosplenomegaly is rare
§
Lymphadenopathy which may be
massive
o
Lung
§
Cyst and bleb formation with
spontaneous PTX
§
Ill-defined diffuse nodular
disease often leading to
fibrosis and honeycombing
·
Prognosis:
spontaneous remissions and exacerbations
Eosinophilic granuloma
·
60-80%
of Histiocytosis X
·
Usually
confined to bone
·
Age
at onset
o
5-10
years highest frequency
o
Male
predominance 3:2
·
Location
o
Calvarium>mandible>spine>ribs>long
bones
o
Most
are monostotic (50-75%)
·
Target
organs
o
Skull
(50%)
§
Diploic space of parietal bone
most often
§
Round or ovoid punched out
lesions with beveled edge
§
Sclerotic margin during healing
phase
§
Beveled edge=hole-within-a-hole
§
Button sequestrum- bony
sequestrum within lytic lesion
§
Axial skeleton (25%)
o
"Vertebra
plana"-"coin-on-edge" (Calve disease)=collapse
of vertebral
body, mostly thoracic
§
Most common cause of vertebra
plana in children
o
Proximal
long bones (15%)
§
Expansile, lytic lesions, mostly
diaphyseal
§
Soft tissue mass
§
Laminated periosteal reaction
o
Lung
(20%)
§
Age peak between 20-40 years
§
Multiple small nodules
§
Predilection for apices
§
Prototype for honeycomb lung
§
Recurrent pneumothoraces (25%)
§
Rib lesions with fractures common
·
Nuclear
Medicine
o
Negative
bone scans in 35%
o
Bone
lesions usually not Ga-67 avid
o
Ga-67
may be helpful in detecting non-osseous lesions
·
Prognosis:
excellent
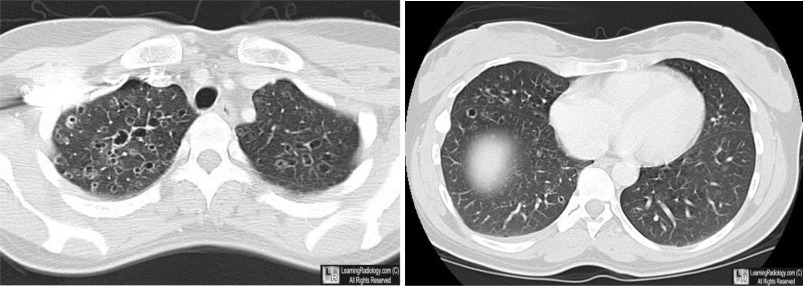
Eosinophilic Granuloma of the Lung. There are multiple, thin-walled cystic structures, greater in the
upper than the lower lobes, characteristic of this disease.
|