
Thymoma
© William Herring, MD, FACR

ThymomaGeneral
Most common anterior mediastinal mass
Most are solid lymphoepithelial tumors ofthe thymus
Some are cystic
About 1/3 are malignant
Rare in children — most common around5th or 6th decade

Thymoma Pathology
Four types (about equal in frequency)
Lymphocytic
Epithelial
Mixed
Spindle cell (Hassall’s corpuscles in thistype)

ThymomasMyasthenia Gravis
50% of patients with thymoma havemyasthenia
15% of patients with myasthenia havethymomas
About 50% improve following removal ofthymoma

Thymomas Clinical
Most are asymptomatic
Many have parathymic syndromes
Mediastinal compression-cough,dysphagia

Parathymic Syndromes
Seen in many patients with thymomas
Myasthenia gravis (50% of patients withthymoma)
Red cell aplasia=aregenerative anemia
Acquired hypogammaglobulinemia
Cushing’s syndrome

ThymomasMalignancy
Surgical evaluation of encapsulation orinvasion is better indicator of malignancythan actual histology
Surgical evaluation of encapsulation orinvasion is better indicator of malignancythan actual histology

Thymomas Malignancy
May spread along pleural reflections to
Posterior mediastinum
Diaphragm
Retroperitoneum
Recurrence rate is high
50% 10 year survival

ThymomasImaging
Oval, round or lobulated soft tissue mass
Sharply demarcated
Usually smaller than teratomas
May displace heart and great vesselsposteriorly
Small percentage (5%) may containcurvilinear or amorphous calcification

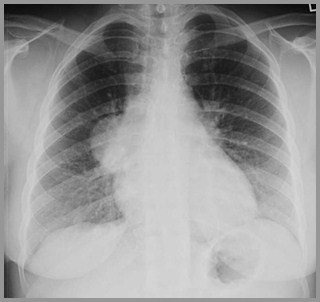
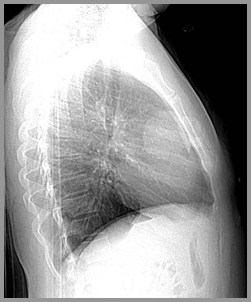
Thymoma-Frontal and Lateral Chestradiographs

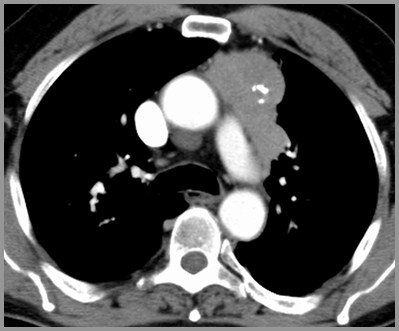
Thymoma-Anterior MediastinalMass with Calcifications

Thymomas MRI Pattern
Isointense on T1
Increased signal on T2

Thymolipomas
Fatty tumors of thymus which constitute2-9% of thymomas
They can be huge
They occur at junction of heart andgreat vessels

The End